- Why This List Matters
- 1. Now Platform
- 2. Table
- 3. Record
- 4. GlideRecord
- 5. Flow Designer
- 6. User Role
- 7. Portal
- 8. Scoped Application
- 9. Form & List
- 10. Update Set
- Bonus Terms Worth Knowing
- Final Thoughts
Before building flows and writing scripts, every ServiceNow beginner should first learn the lingo. Here’s your 2025 ready cheat sheet.
Why This List Matters
When you’re new to ServiceNow, it’s easy to get lost in a blur of modules, acronyms, and frameworks. But mastering the vocabulary is step one to mastering the platform.
These aren’t just buzzwords, they’re the building blocks of the Now Platform. So whether you’re aiming to become a ServiceNow Developer, Admin, or Architect, this glossary style guide will give you clarity and confidence.
1. Now Platform
Think of this as the core technology engine behind every ServiceNow product/app/plugin, from ITSM and HRSD to CSM and beyond. It’s a Platform as a Service (PaaS) foundation that enables you to automate workflows, build portals, and drive enterprise operations.
Why you should care: Everything you touch in ServiceNow runs on the Now Platform.
2. Table
A table is where your data lives. Each app, like Incidents or Employees, is backed by a table, and they can be extended, related, or customized.
Pro tip: The task table is the parent for many process driven records like Incident, Change, and Request.
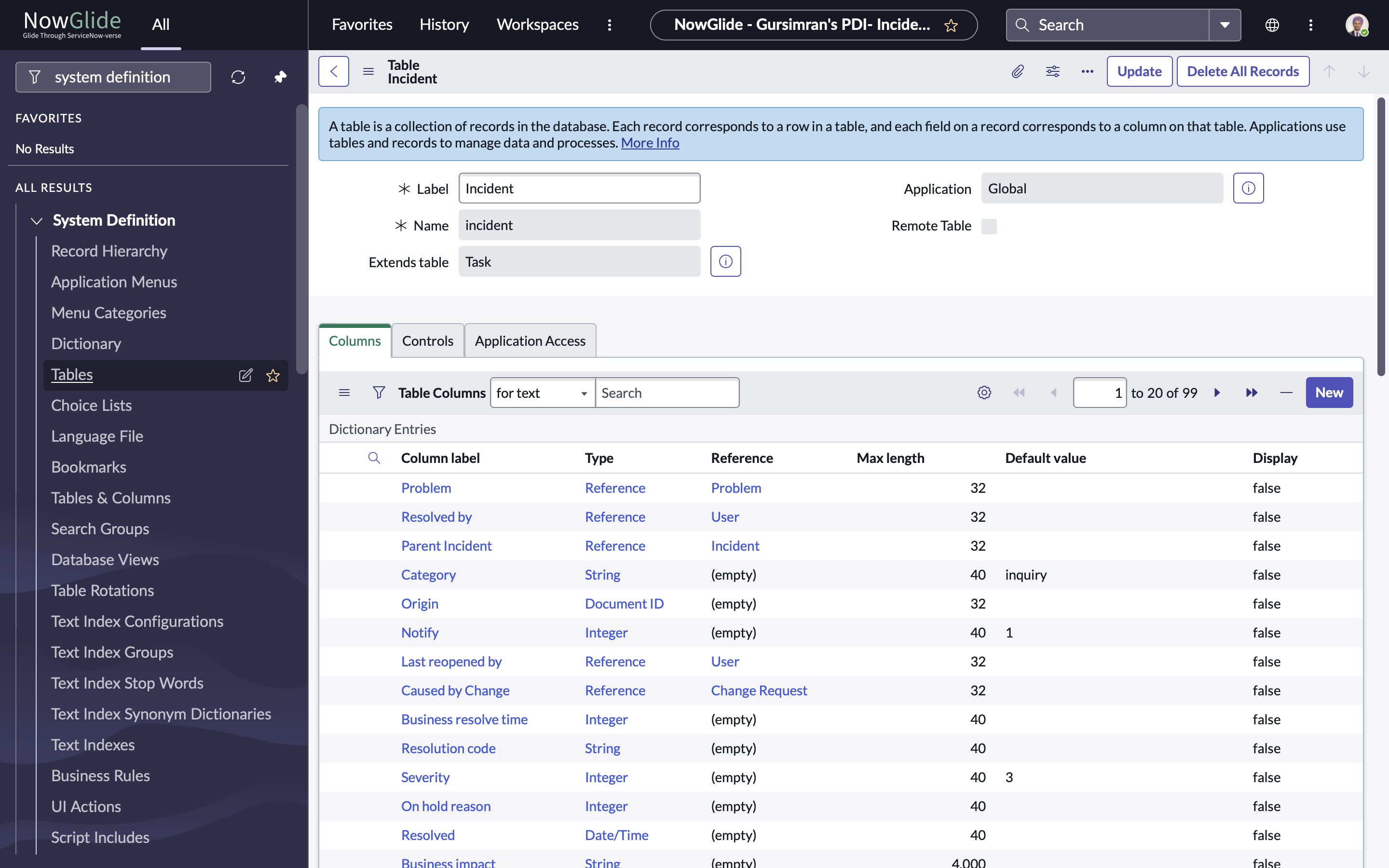
You might’ve noticed I referred to things like Incidents and Employees as apps. That’s intentional, and honestly, it’s one of the most ingenious design patterns I’ve seen in ServiceNow. Everything in ServiceNow is highly modular. You have Products (like ITSM, HRSD, CSM), which contain Applications (like Incident Management, Change Management), which in turn rely on Plugins (like Document Intelligence, Integration Hub). And then, at the heart of it all, are Tables, where the data lives. Each application sits inside its own scope, like its own sandbox or prison cell, isolated by default, and not allowed to interact with others unless explicitly permitted. This scoped architecture makes development safer, cleaner, and more maintainable. More on this later!
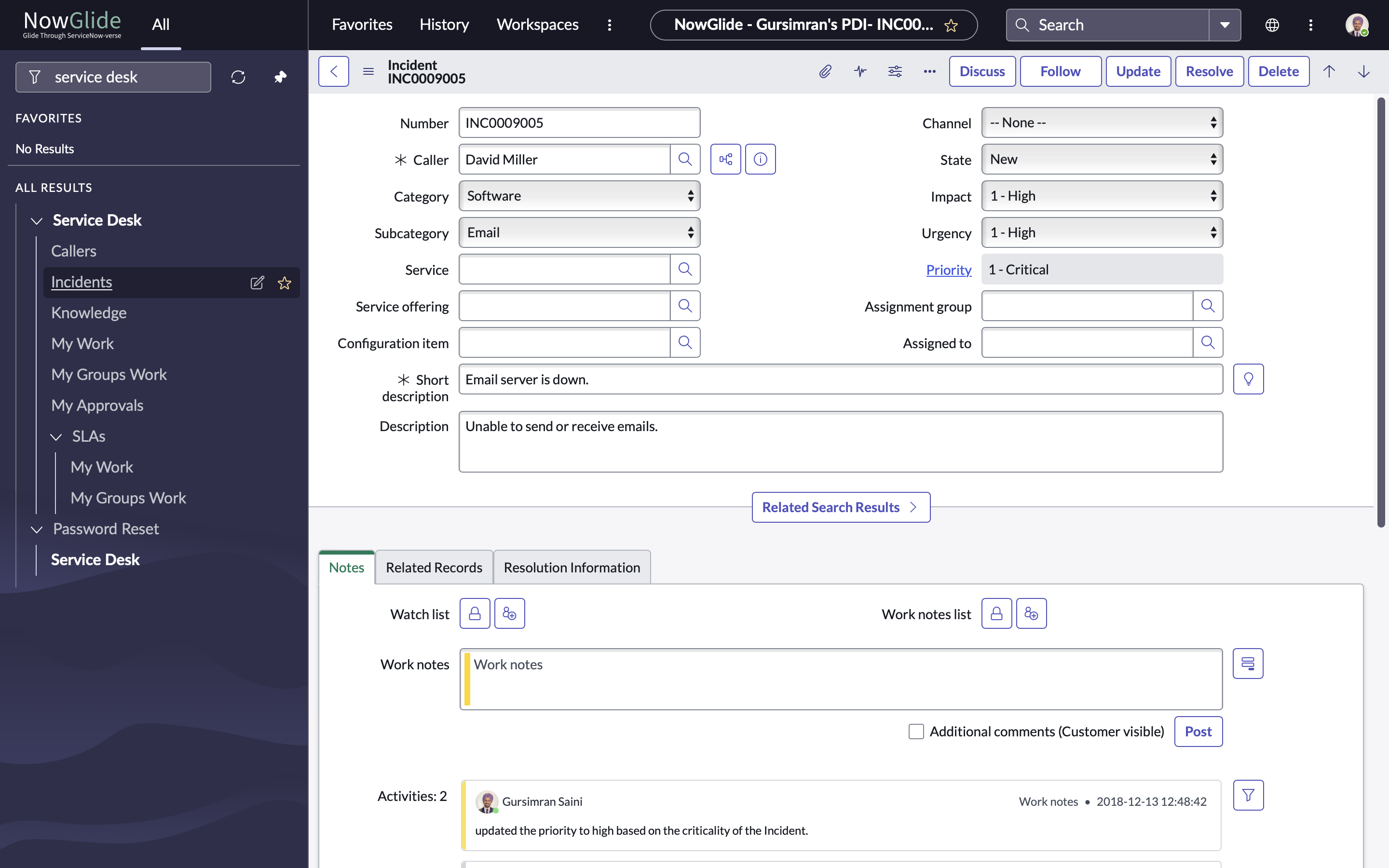
3. Record
Every entry in a table is a record. Think: one Incident, one User, one HR Case.
Real world analogy: A record is like a row in Excel, with columns as fields.
4. GlideRecord
A powerful JavaScript API used for querying and manipulating records in the database.
Why beginners love it: You’ll use it in Business Rules, Script Includes, or anywhere you want to “talk” to the database.
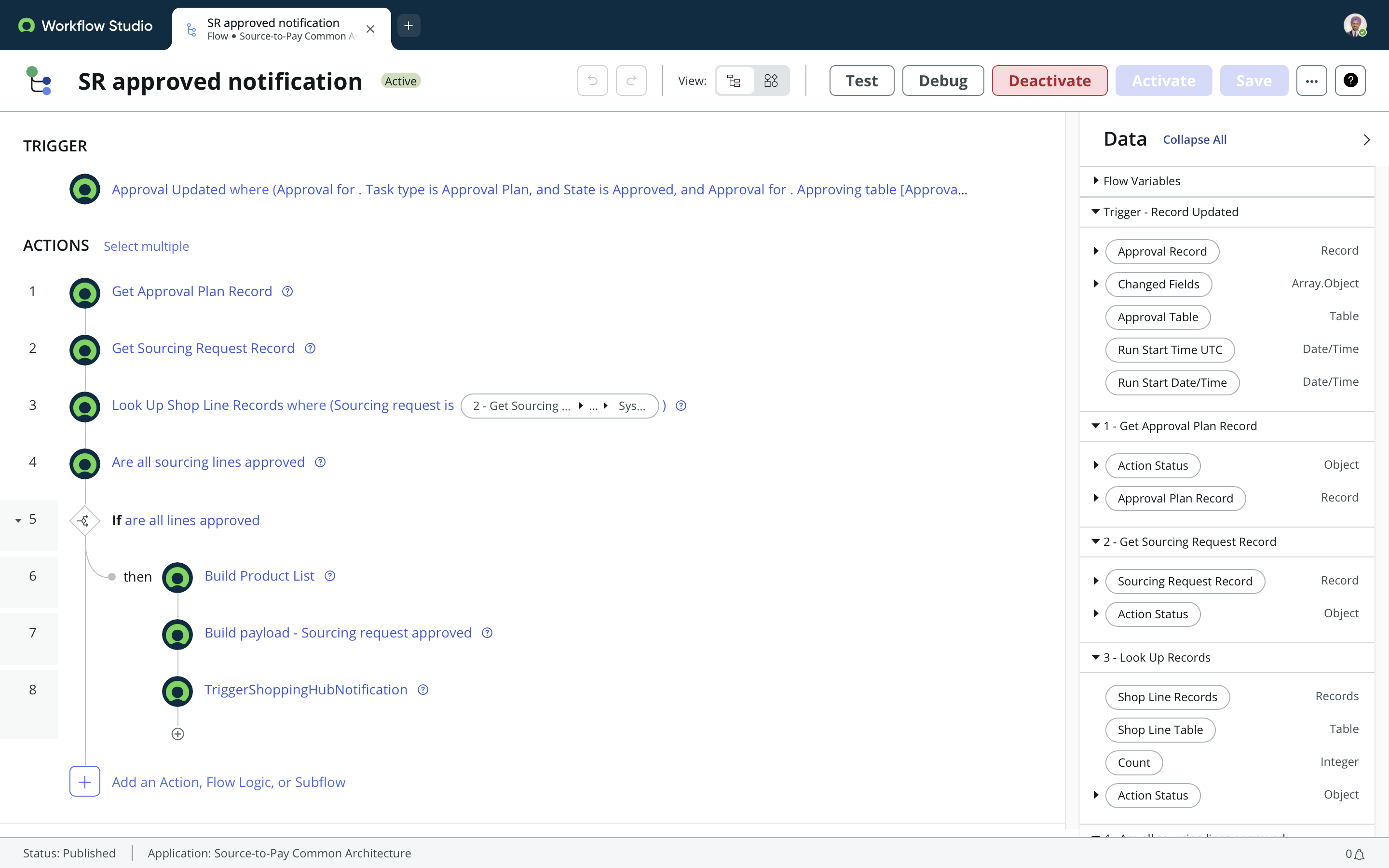
5. Flow Designer
ServiceNow’s low code automation tool that lets you build logic with clicks instead of code.
2025 update: Most new implementations prefer Flow Designer over legacy Workflow Editor.
6. User Role
Controls what a user can see or do. For example, only users with admin or itil roles can access Incident forms.
What to remember: Misconfigured roles are one of the top causes of “why can’t I see this?” confusion.
7. Portal
Portals are the user friendly web interfaces built on Service Portal or Next Experience (UI Builder). For example, the Employee Center or Customer Service Portal.
Bonus: They’re fully customizable, add widgets, logic, and even branding. You can view the list of available (installed) portals in your instance by navigating to sp_portal.list via the Filter Navigator.
8. Scoped Application
A modular “package” of functionality with its own namespace. Scoped apps help you isolate logic, tables, and scripts cleanly.
Why you’ll need this: Most modern ServiceNow development uses scoped apps, especially in HR, CSM, and custom solutions.
9. Form & List
The two most common UI layouts.
- List = table view
- Form = record view
10. Update Set
A container that tracks configuration changes for moving between environments (like Dev → Test → Prod).
Be cautious: Update Sets don’t capture everything, like data, or some Flow Designer components. Know what’s in and what’s not.
Bonus Terms Worth Knowing
There are many terms in ServiceNow that didn’t make the top 10 list, but still pack a punch in daily use. Here are a few more that every curious beginner should explore:
- Scoped Application - Modular package for isolated development.
- UI Policy - Control form field visibility, read only state, and requirement rules.
- Service Portal - The friendly UI layer of ServiceNow.
- Access Control (ACL) - Who sees or changes what, everywhere.
- Business Rule - Server side logic that drives automation.
- Script Include - Reusable server side scripts for maintainable code.
- UI Action - Buttons or actions (on Forms and Lists) that help users interact better.
- Service Catalog - One stop shop for requesting IT and business services and products.
These bonus terms often reveal their true importance as you dive deeper into the platform.
Final Thoughts
When I first pivoted from Oracle B2C Service to ServiceNow, these terms became my anchor. If you’re just starting in 2025, trust me, learning the vocabulary early will make everything else feel a lot more natural.
Written by: Gursimran Singh Saini - Assistant Director @ EY. Exploring the ServiceNow platform and modern enterprise automation. I write to learn, and share to remember.
Have thoughts to share? Join the discussion below!